Enlarged Prostate Treatment: Effect
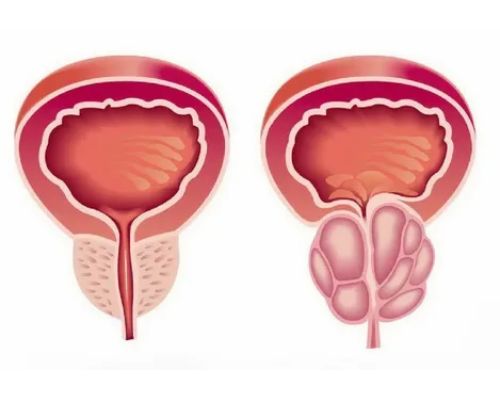
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), commonly known as an enlarged prostate, is a common condition among aging men. While it is not cancerous, it can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms that impact daily life. Fortunately, several effective treatment options are available to manage BPH and improve quality of life. This article explores medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and surgical options for treating an enlarged prostate.
Understanding BPH:
BPH occurs when the prostate gland grows larger, pressing against the urethra and leading to urinary problems. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Weak urine stream or difficulty starting urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Incomplete bladder emptying
Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
For mild cases, lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms:
- Limit Fluid Intake Before Bed: Reducing evening fluid consumption can decrease nighttime urination.
- Reduce Caffeine and Alcohol: These substances can irritate the bladder and increase urgency.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in physical activity can reduce BPH symptoms.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening pelvic muscles may help with urinary control.
- Medications
If lifestyle changes are insufficient, medications can be prescribed:
- Alpha-Blockers (e.g., Tamsulosin, Doxazosin): These relax prostate muscles, improving urine flow.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (e.g., Finasteride, Dutasteride): These reduce prostate size by lowering hormone levels that cause prostate growth.
- Combination Therapy: In some cases, both types of medications are used together for better symptom relief.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures
For patients who do not respond to medication, minimally invasive treatments are available:
- Transurethral Microwave Therapy (TUMT): Uses microwave energy to shrink excess prostate tissue.
- UroLift System: A procedure that lifts and holds enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra.
- Water Vapor Therapy (Rezum): Delivers steam to shrink prostate tissue, improving urine flow.
- Surgical Treatments
When other treatments fail, surgery may be required:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): A common procedure where excess prostate tissue is removed using an electric current or laser.
- Prostatectomy: In severe cases, part or all of the prostate may be removed.
- Laser Surgery (HoLEP or PVP): Uses laser energy to remove excess prostate tissue with minimal bleeding.
When to See a Doctor
Men experiencing severe urinary symptoms, frequent infections, or complications such as bladder stones should seek medical advice. Early treatment can prevent worsening symptoms and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
Enlarged prostate treatment varies depending on symptom severity and overall health. Lifestyle modifications, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery offer effective options for managing BPH. Consulting a healthcare professional ensures the best approach for individual needs, allowing men to lead healthier and more comfortable lives.









